PyDeck in Jupyter Notebook
The PyDeck (opens in a new tab) is a package for visualization of spatial data.
It can be used in Mercury.
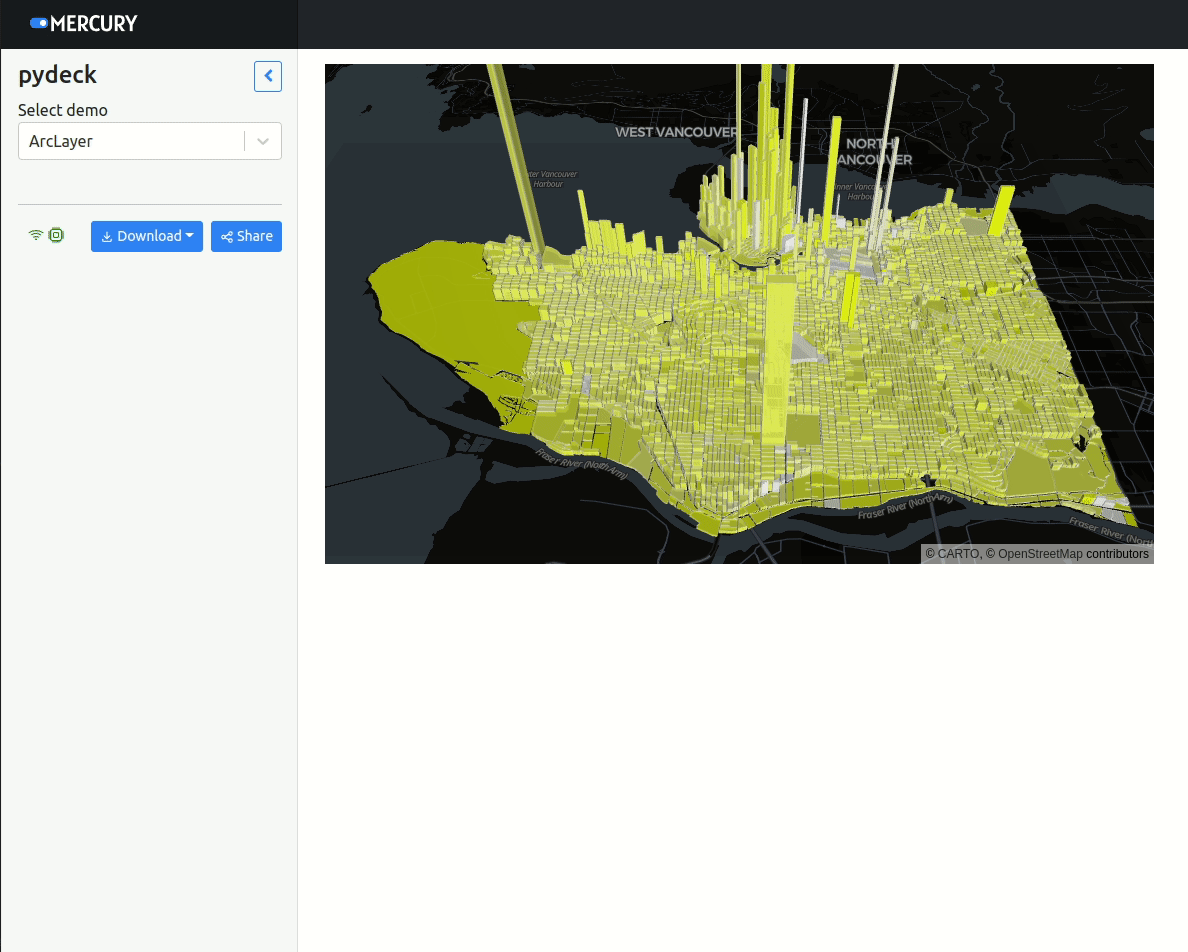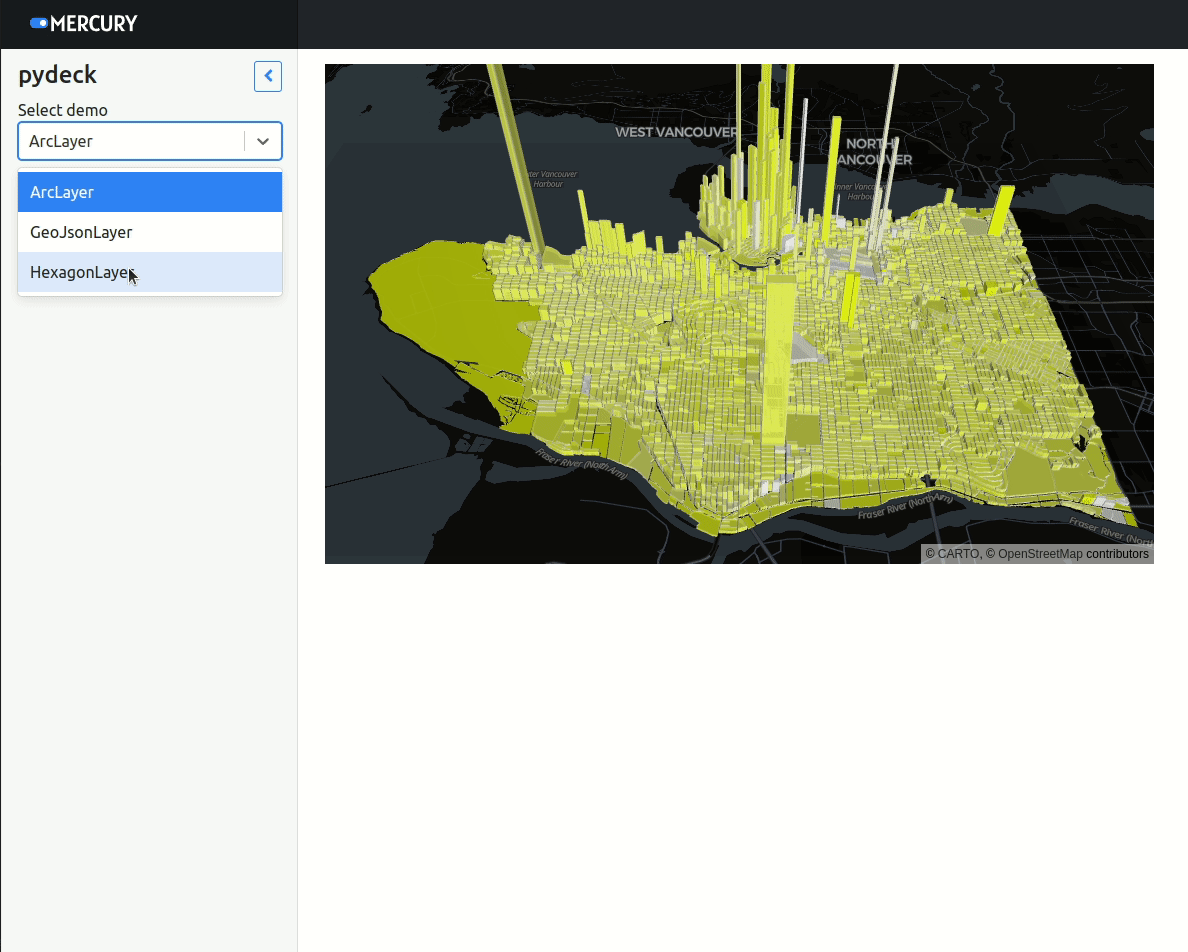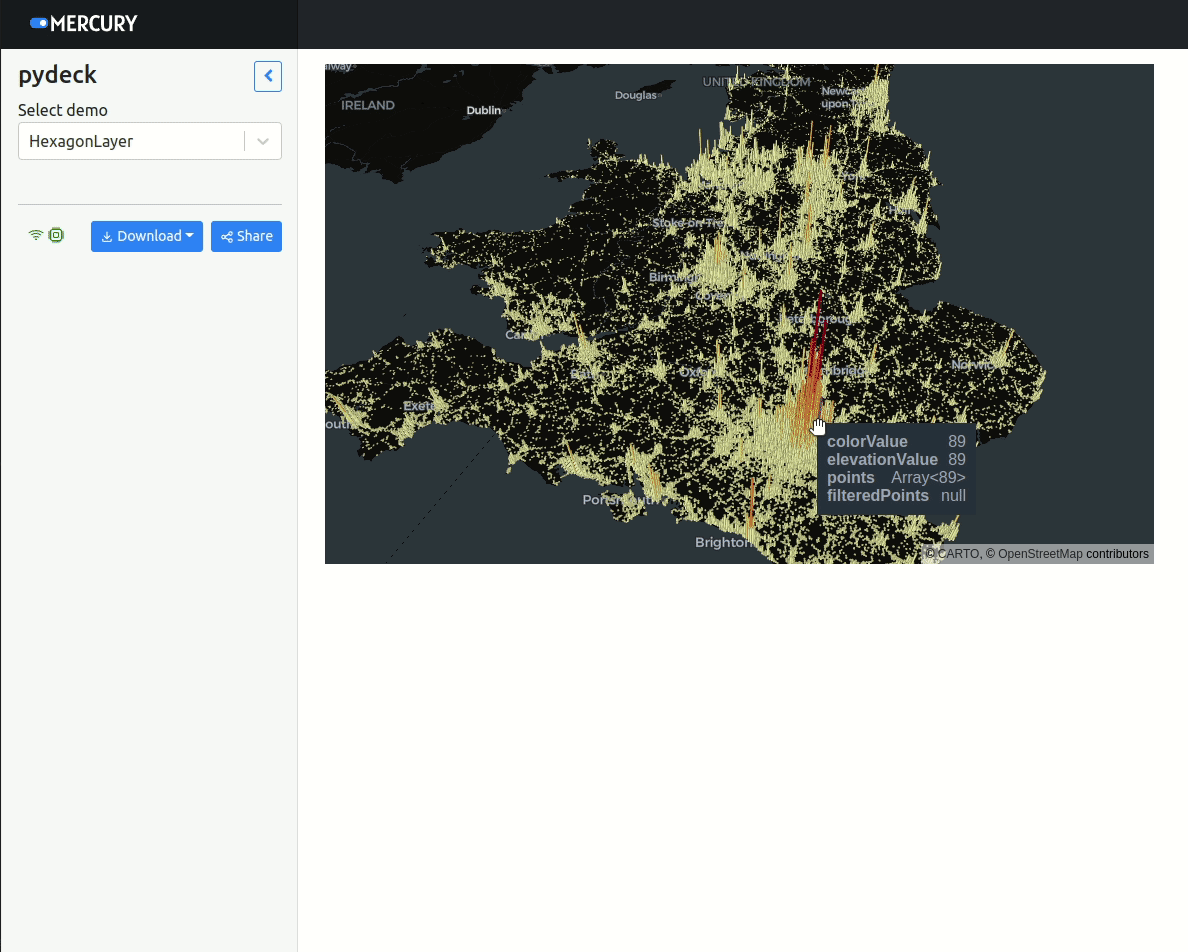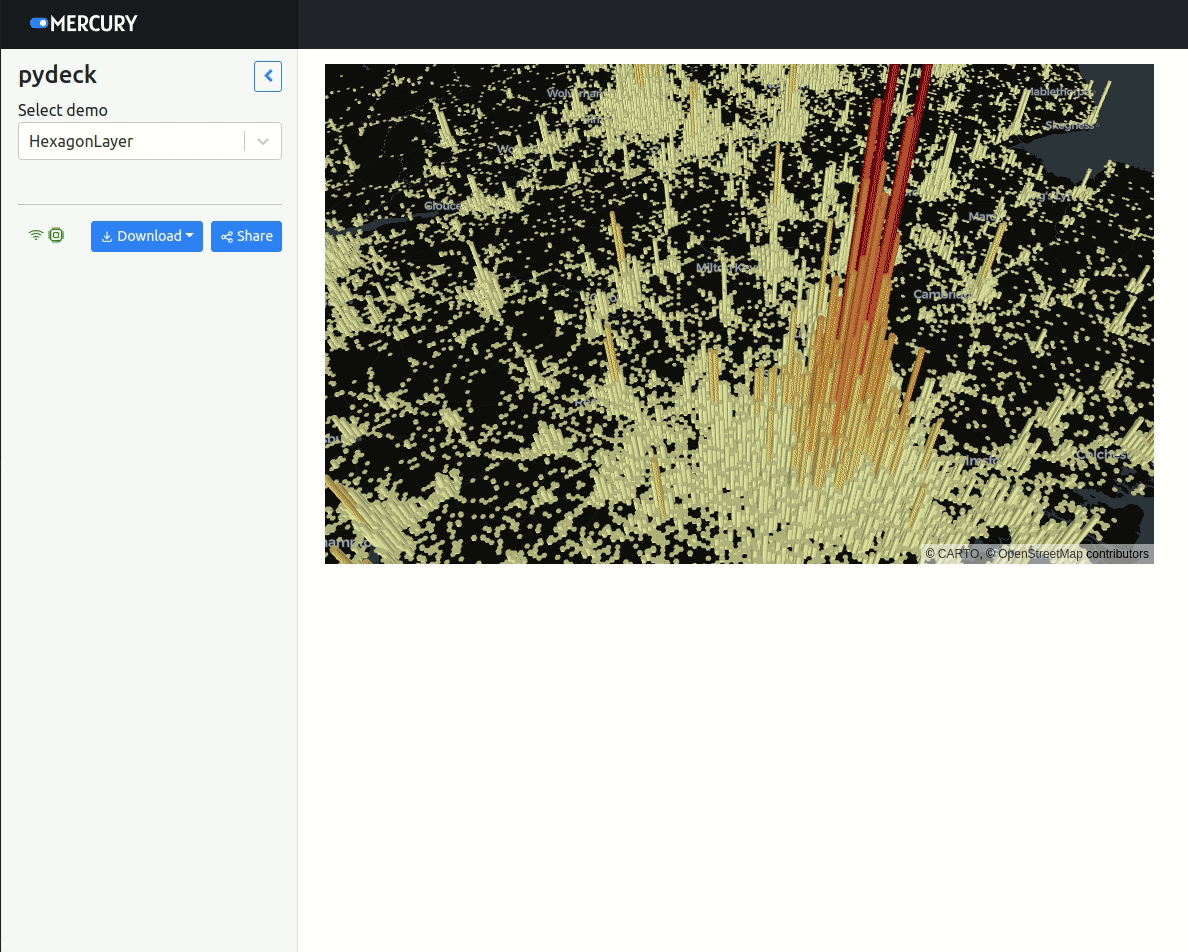
Please notice that PyDeck allows for two-way interaction in Jupyter Notebook. However, in Mercury it can be only used to display data (one-way communication).
Required packages
You will need the following packages to run this example:
pydeck
pandas
mercuryNotebook
We will build a simple web app that display different demos of PyDeck. It is based on code from PyDeck gallery (opens in a new tab).
Import required packages:
import pydeck as pdk
import pandas as pd
import mercury as mrAdd Select widget to select example:
demo = mr.Select(label="Select demo", choices=["ArcLayer", "GeoJsonLayer", "HexagonLayer"])Create first demo:
if demo.value == "ArcLayer":
DATA_URL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/visgl/deck.gl-data/master/examples/geojson/vancouver-blocks.json"
LAND_COVER = [[[-123.0, 49.196], [-123.0, 49.324], [-123.306, 49.324], [-123.306, 49.196]]]
INITIAL_VIEW_STATE = pdk.ViewState(latitude=49.254, longitude=-123.13, zoom=11, max_zoom=16, pitch=45, bearing=0)
polygon = pdk.Layer(
"PolygonLayer",
LAND_COVER,
stroked=False,
# processes the data as a flat longitude-latitude pair
get_polygon="-",
get_fill_color=[0, 0, 0, 20],
)
geojson = pdk.Layer(
"GeoJsonLayer",
DATA_URL,
opacity=0.8,
stroked=False,
filled=True,
extruded=True,
wireframe=True,
get_elevation="properties.valuePerSqm / 20",
get_fill_color="[255, 255, properties.growth * 255]",
get_line_color=[255, 255, 255],
)
r = pdk.Deck(layers=[polygon, geojson], initial_view_state=INITIAL_VIEW_STATE)Create second demo:
if demo.value == "GeoJsonLayer":
DATA_URL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ajduberstein/sf_public_data/master/bay_area_commute_routes.csv"
# A bounding box for downtown San Francisco, to help filter this commuter data
DOWNTOWN_BOUNDING_BOX = [
-122.43135291617365,
37.766492914983864,
-122.38706428091974,
37.80583561830737,
]
def in_bounding_box(point):
"""Determine whether a point is in our downtown bounding box"""
lng, lat = point
in_lng_bounds = DOWNTOWN_BOUNDING_BOX[0] <= lng <= DOWNTOWN_BOUNDING_BOX[2]
in_lat_bounds = DOWNTOWN_BOUNDING_BOX[1] <= lat <= DOWNTOWN_BOUNDING_BOX[3]
return in_lng_bounds and in_lat_bounds
df = pd.read_csv(DATA_URL)
# Filter to bounding box
df = df[df[["lng_w", "lat_w"]].apply(lambda row: in_bounding_box(row), axis=1)]
GREEN_RGB = [0, 255, 0, 40]
RED_RGB = [240, 100, 0, 40]
# Specify a deck.gl ArcLayer
arc_layer = pdk.Layer(
"ArcLayer",
data=df,
get_width="S000 * 2",
get_source_position=["lng_h", "lat_h"],
get_target_position=["lng_w", "lat_w"],
get_tilt=15,
get_source_color=RED_RGB,
get_target_color=GREEN_RGB,
pickable=True,
auto_highlight=True,
)
view_state = pdk.ViewState(
latitude=37.7576171,
longitude=-122.5776844,
bearing=45,
pitch=50,
zoom=8,
)
TOOLTIP_TEXT = {"html": "{S000} jobs <br /> Home of commuter in red; work location in green"}
r = pdk.Deck(arc_layer, initial_view_state=view_state, tooltip=TOOLTIP_TEXT)The last demo:
if demo.value == "HexagonLayer":
HEXAGON_LAYER_DATA = (
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/visgl/deck.gl-data/master/examples/3d-heatmap/heatmap-data.csv" # noqa
)
# Define a layer to display on a map
layer = pdk.Layer(
"HexagonLayer",
HEXAGON_LAYER_DATA,
get_position=["lng", "lat"],
auto_highlight=True,
elevation_scale=50,
pickable=True,
elevation_range=[0, 3000],
extruded=True,
coverage=1,
)
# Set the viewport location
view_state = pdk.ViewState(
longitude=-1.415,
latitude=52.2323,
zoom=6,
min_zoom=5,
max_zoom=15,
pitch=40.5,
bearing=-27.36,
)
# Render
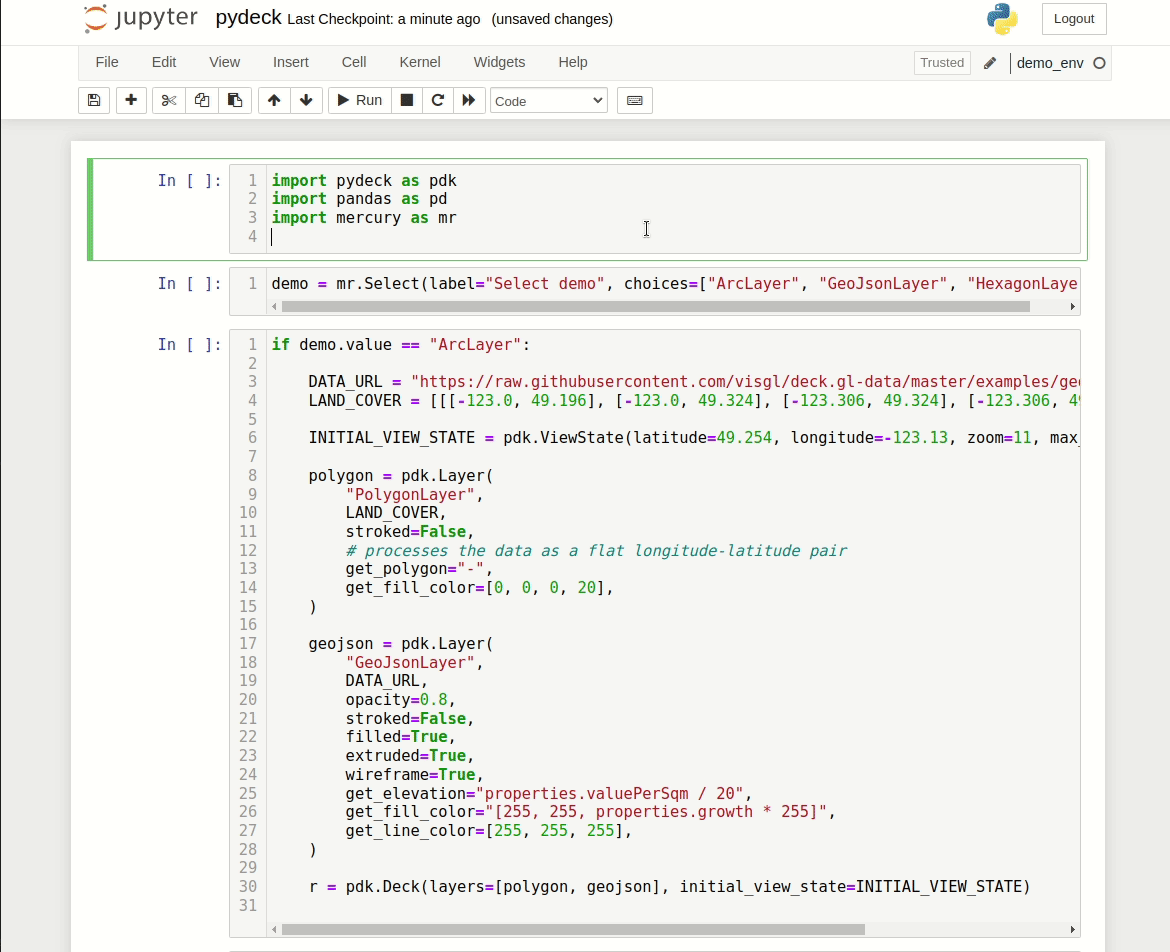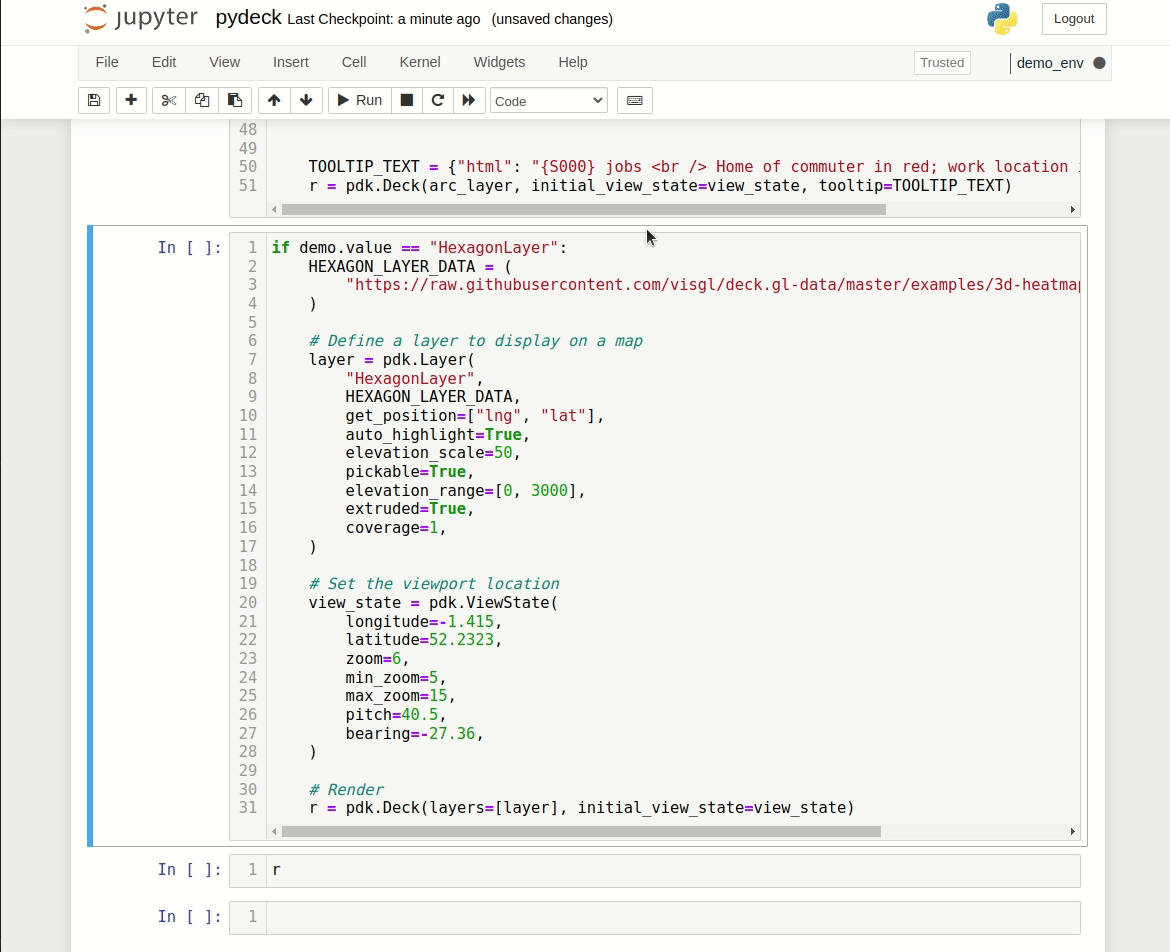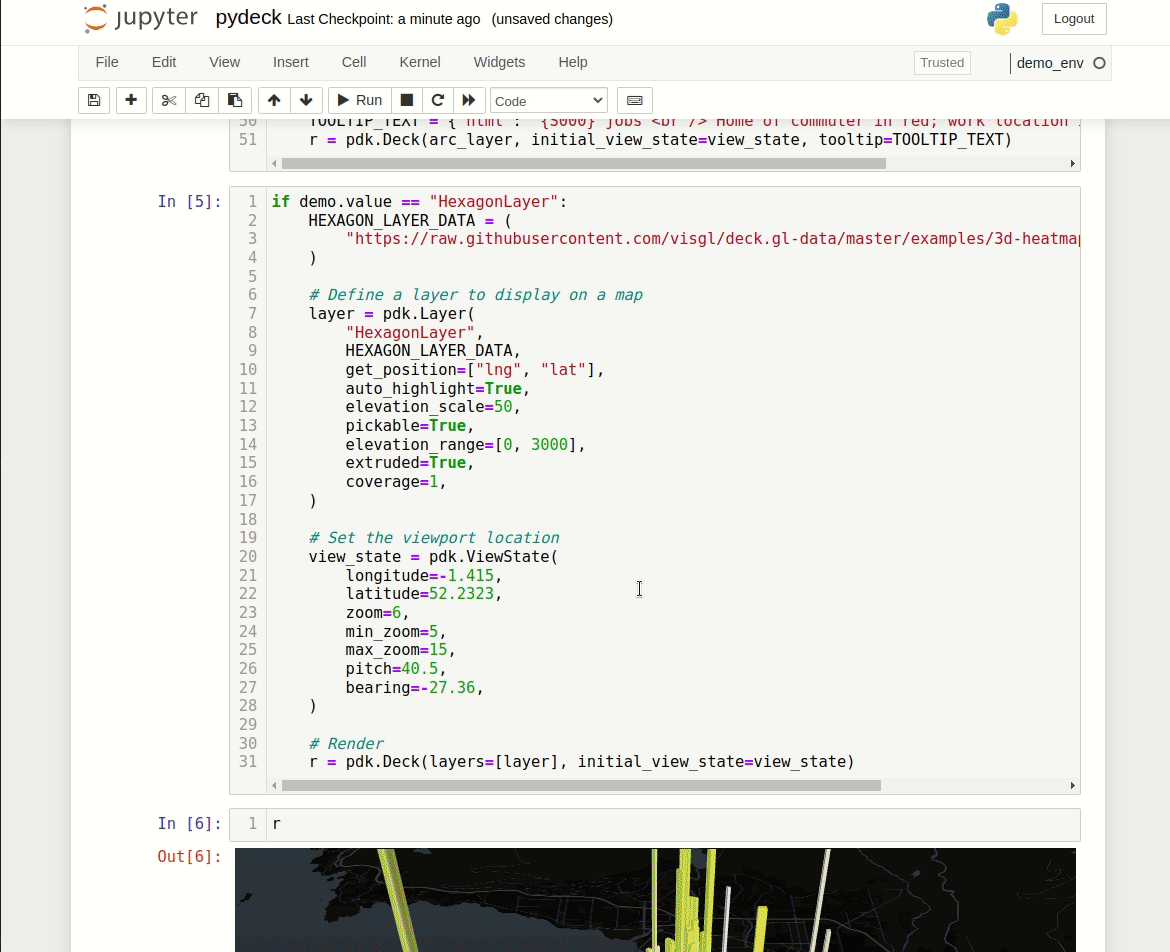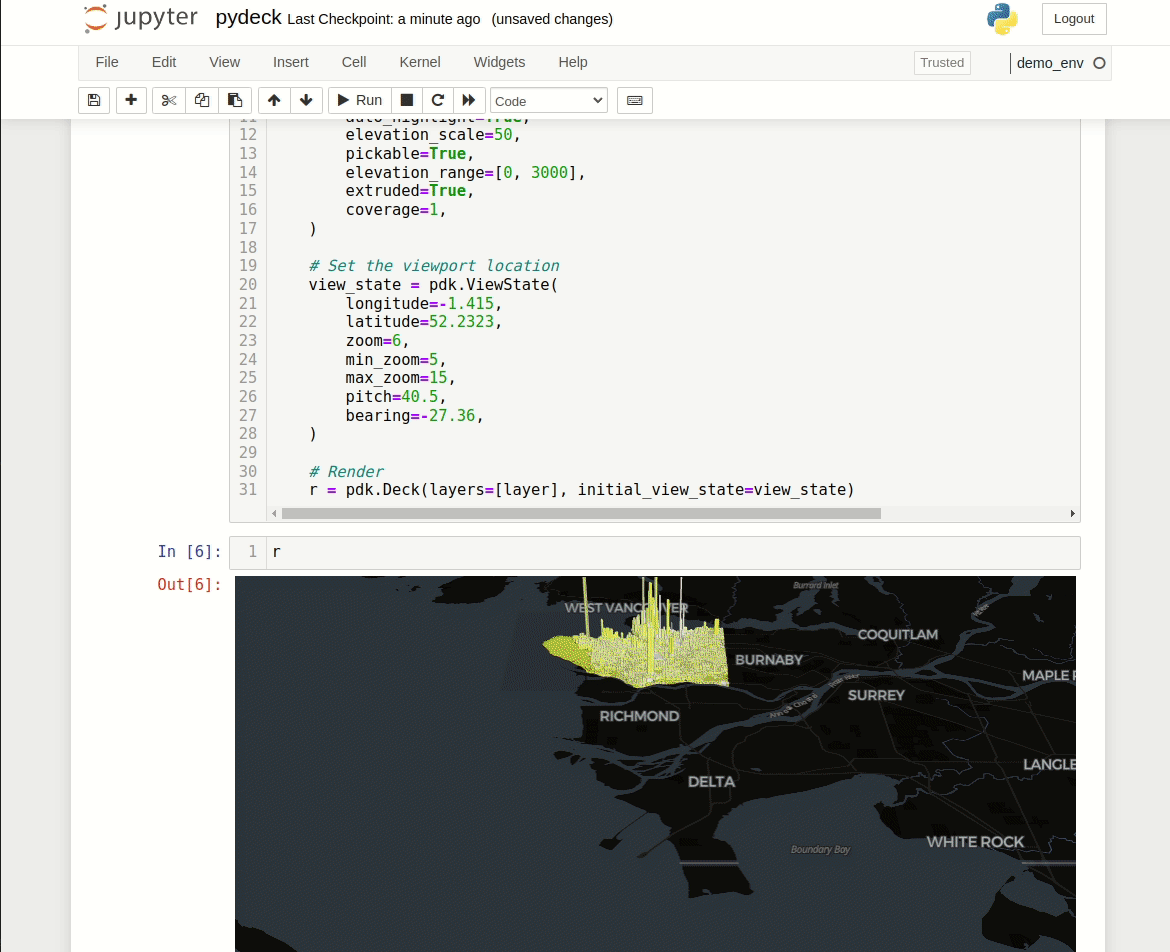
r = pdk.Deck(layers=[layer], initial_view_state=view_state)Display the PyDeck map:
rYes, just one letter. It will display out PyDeck object that was initialized depending on selected widget value.
Mercury App
Please start a Mercury Server in the same directory as your notebook:
mercury runPlease open the website with address http://127.0.0.1. You should see the web app with PyDeck demo running.
The notebook from this example is available in the mercury-examples (opens in a new tab) repository.