Table
The Table widget displays data in a structured, interactive tabular format. It supports column sorting (ascending/descending), quick filtering, and row selection for easier data exploration.
Import
Section titled “Import”from mercury import TableTo use the Table widget, you only need to provide data. It works best with DataFrames (pandas or polars), but you can also pass lists of dict or dicts.
Example data
import pandas as pd
countries = ["Poland", "Germany", "France"]
df = pd.DataFrame({ "Country": [countries[i % 3] for i in range(100)], "Year": [2020 + (i % 10) for i in range(100)], "GDP": [500 + (i * 25) for i in range(100)],})Code
t = Table(df)Preview
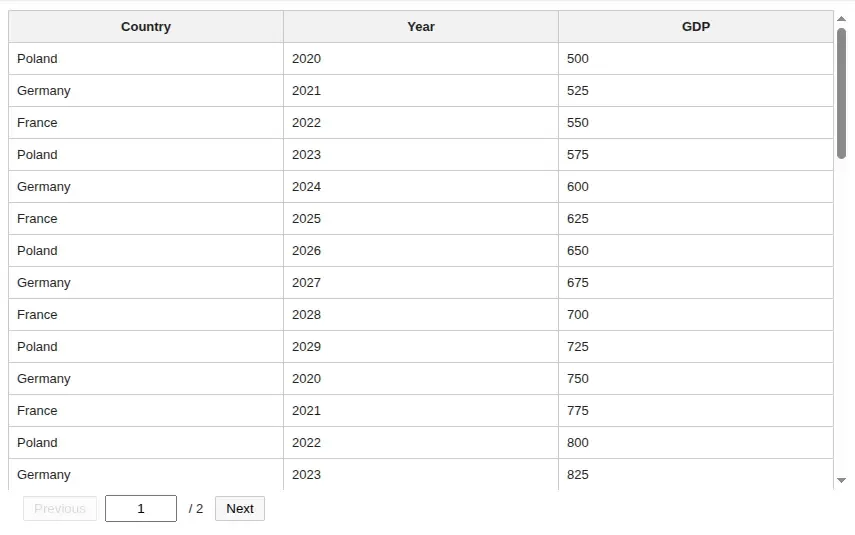
Table with features
Section titled “Table with features”You can easily add more features to your table, such as row selection or filtering.
Code
t = Table(df, search=True, select_rows=True)Preview
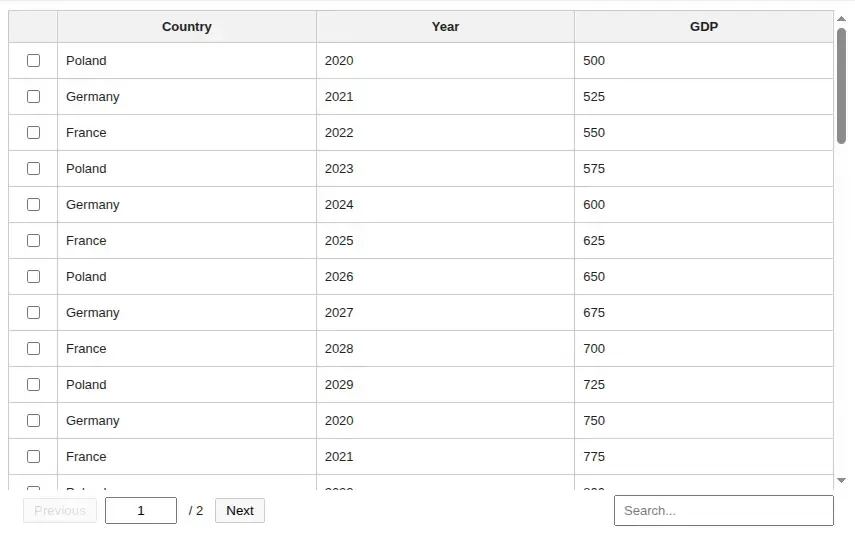
Get selected rows
Section titled “Get selected rows”After enabling row selection, you may want to access all selected rows in one place — this is very easy to do.
Code
# t is the variable that you assign the Table tot.selected_rowsCustomize your Table
Section titled “Customize your Table”You can also customize the Table’s appearance by changing the page size (number of rows per page) or adjusting its width.
Code
t = Table(df, search=True, select_rows=True, page_size=20, width="700px")Preview
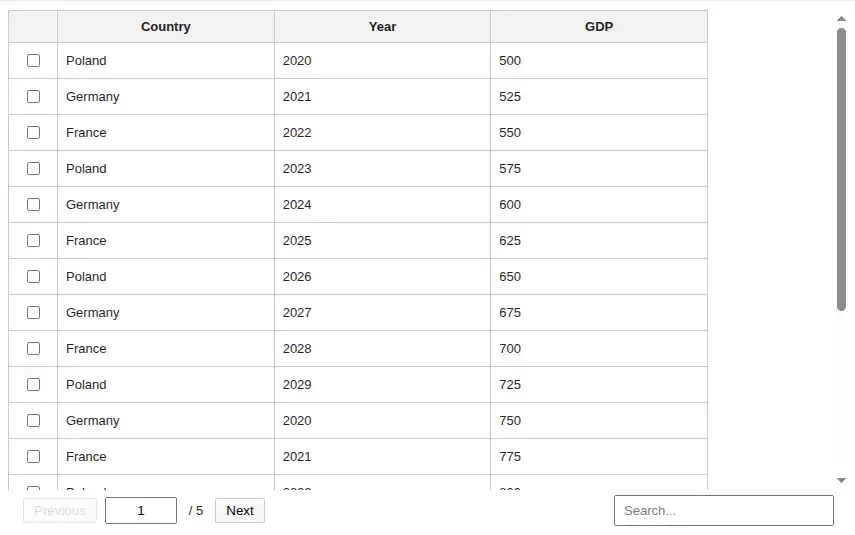
Table Props
Section titled “Table Props”data (required)
Section titled “data (required)”type: DataFrame or list[dict] or dict
The dataset displayed in the table. Accepts pandas/polars DataFrames or standard Python structures like lists of dictionaries.
page_size
Section titled “page_size”type: Integer
Sets how many rows are shown on a single page. Default is 50.
select_rows
Section titled “select_rows”type: boolean
Enables selecting rows in the table. It’s off by default (False).
search
Section titled “search”type: boolean
Enables the search bar and allows filtering table. It’s off by default (False).
type: string
Sets the width of the table component. Accepts values like 100%, 800px, or other valid CSS size units. Default is 100%.